React State Management
REACT STATE MANAGEMENT
Why?
리액트의 상태관리는 useState만으로 하기에는 힘들다.
상태가 많아지고 전달해야 할 props가 늘어난다면 props를 계속 전달해줘야 하는 불편함도 생긴다. 또한 어디서 어떤 상태를 변경하고 있는지 이를 추적하고 이해하기 어려울수 있다.
리액트에 효과적인 상태관리 방법은 무엇인지 알아야할 필요가 있다.
Props drilling
컴포넌트 간 state 공유 방식에서 발생하는 문제이다.
해당 state가 필요하지 않는 중간 영역 컴포넌트에도 props로 전달해 주어야 해서 복잡성이 커지고 불필요한 동작이 생기는 문제가 있다.
개선 방법
- Context API
왼쪽은 Props drilling, 오른쪽은 Context API을 사용한 state 공유
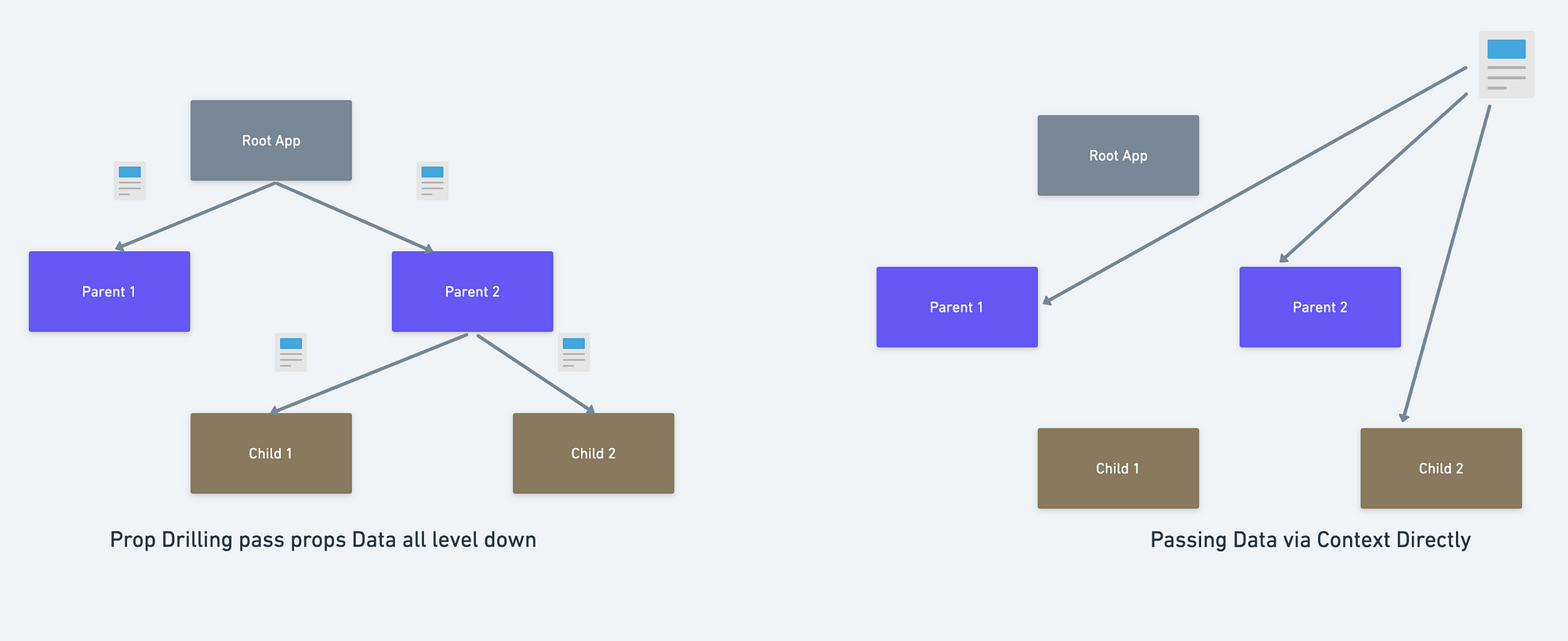
코드상으로는 중간 영역에서 받아서 전달할 필요가 없지만, 실제로는 결국 props 로 전달되는 방식이다.
- state 관리 라이브러리
global store(Mobx, Redux 등)를 통해서 관리할 수 있다.
Redux는 Flux아키텍쳐 기반으로, global에 여러개의 store를 만들어서 관리한다.
데이터 변경 로직이 view와 분리된다.
Flux Architecture
React는 View 렌더링에 집중하는 라이브러리이기 때문에 다양한 Store(Model)에 연결가능하다.

Redux
Flux Architucture를 따른다.
single source of truth
unidirectional data flow, one way data binding
한개의 store를 통한 데이터 관리와, 데이터 전달을 목적으로 한다.
학습비용이 큰 편이지만, 대규모 store처리를 하기 위해서는 좋은 선택지이다.
Flow
view가 dispatcher에 action을 전달하고, store에서 데이터 변경을 관리하고, view는 store를 구독하는 방식이다.
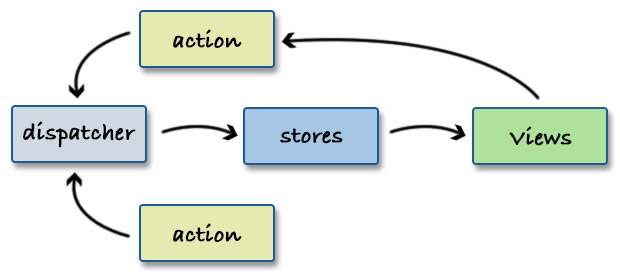
[예제]
view
dispatch({
type: 'deposit',
payload: 10
})
reducer
switch (action.type) {
case "deposit":
return {
action.payload
}
....
.....
Immutable data
reducer의 상태변경 방법은 state를 직접 변경하기보다는, immutable 방식으로 변경하는 것이 좋다.
Immutable 방식으로 변경하면 이전 node와 변경할 node를 비교할때 shallow equality checking을 할 수 있어서 상태변경을 빠르게 알아챌 수 있다.
[예시] 배열의 특정 원소를 immutable 방식으로 업데이트 하기 [a,b,c,d] -> [a,b,e,d]
export const immutable = {
updateArrayElement(source, target, attr, value) {
const updatedItem = source.filter(item => item.id === +target)[0];
updatedItem[attr] = value;
const updatedItemIndex = (source.indexOf(updatedItem));
return Object.assign([...source], { [updatedItemIndex]: updatedItem });
}
}
Context API
props를 계속 내려줘야 하는 불편함을 없앴다.
Provider와 Consumer관계를 통해서, props전달 없이 필요한 자식 component에서 필요한 Provider를 직접 불러서 사용하면 된다.
useState값을 담을수도 있고, 아래 나오는 useReducer의 값을 담을 수도 있다.
[예시] Context API에 useReducer의 dispatch와 value 전달하기
useReducer를 활용해서 상태 관리를 할 때 view component와 좀 더 느슨한 관계를 만들 수 있다.
Context API를 활용해서 provider / consumer 관계를 만들어서 특정 context의 store정보를 접근할 수 있다.
[Provider]
상태, 즉 데이터를 관리하는 제공자이다. (Model역할)
createContext 메서드를 통해서 Context Component 객체를 생성한다.
Context provider는 useReducer의 값과 dispatch메서드를 value로 갖고 있다.
[예시]
const postReducer = (posts, { type, payload }) => {
switch (type) {
case 'setInitial':
return payload;
case 'add':
return [...posts, new makeItem({ title: payload, id: posts.length + 1 })];
case 'addPicked':
return _.immutable.updateArrayElement(posts, payload, "picked", true);
case 'deletePicked':
return _.immutable.updateArrayElement(posts, payload, "picked", false);
default:
break;
}
}
export const PostsContext = React.createContext();
const App = () => {
...
return (
<PostsContext.Provider value=>
<PickedItems posts={posts} />
<button onClick={addItemHandler}>ADD</button>
<Items posts={posts} />
</PostsContext.Provider>
)
}
[consumer]
Hooks에서는 편리하게 Context API를 사용할 수 있고, consumer에서 useContext API를 제공한다.
const PickedItemTitle = (props) => {
const { posts } = useContext(PostsContext);
const pickedTitles = posts.filter(post => post.picked).map(picked => {
return { title: picked.title, id: picked.id }
});
return (
<ul>
{pickedTitles && pickedTitles.map(({ title, id }) =>
<TitleStyle key={id}>{title}</TitleStyle>
)}
</ul>)
}
useReducer 훅을 사용하면 dispatch메서드를 통해서 Redux와 비슷하게,
action을 전달하는 방식으로 event를 발생시킬 수 있다.
const addItemHandler = () => {
dispatch({ type: 'add', payload: 'crororong' });
}
Recoil
-
Hooks 만으로 상태관리를 할 때 생기는 불편함을 해결해줄 수 있다.
-
atom이라는 독립적인 store를 여러개 만들 수 있다.

- Context API는 연결된 컴포넌트들 ReRendering 하지만 Recoil 은 연결된 컴포넌트들이 불필요하게 렌더링되지 않는다.
[예시]
Atom.js
import { atom } from "recoil";
export const numState = atom({
key: "count",
default: 1
});
export const clickCountAtom = atom({
key: "clickCount",
default: 0
});
export const authenticationAtom = atom({
key: "authentication",
default: false
});
View.js
import { useRecoilState } from "recoil";
import { clickCountAtom, authenticationAtom } from "./atoms/atoms";
const ClickCountView = () => {
console.log("clickCountvIEW CALLED");
const [clickCount] = useRecoilState(clickCountAtom);
return (
<>
<div>클릭 횟수 : {clickCount}</div>
<PrivateView />
</>
);
};
react-query & useSWR
- 상태를 공유중인 컴포넌트들의 부모에서 서버 data fetching하지 말고 각각 컴포넌트에서의 관리한다.
- URL기준으로 캐시해서 중복 요청을 하지 않는다.
- 적절한 시간의 데이터 갱신을 위해 cache를 사용한 prefetch을 지원한다.
[예시] (get method)
export const Body = () => {
const { isLoading, isError, data , error} = useQuery('labels', getLabels, {
// Refetch the data every second
refetchInterval: 7000,
});
if (isLoading) {
return <span>Loading...</span>
}
if (isError) {
return <span>Error: {error.message}</span>
}
return (
<ul>
{data.map((todo) => (
<LabelList key={todo.id} {...todo} />
))}
</ul>
);
};
[예시] mutation (post, put, delete 등 method)
//fetch util
const updateLabel = (id, inputValue) => {
return fetch(`http://localhost:3001/label/${id}`, {
method: 'PATCH',
headers: { 'Content-Type': 'application/json' },
body: JSON.stringify({ description: inputValue }),
}).then((res) => res.json());
};
//Component
export const LabelList = ({ id, name, description }) => {
const queryClient = useQueryClient();
const [isEditingMode, setEditingMode] = useState(false);
const [inputValue, setInputValue] = useState('');
const PatchMutation = useMutation((idx) => updateLabel(idx, inputValue), {
onSuccess: (data, variables, context) => {
queryClient.invalidateQueries('labels');
setEditingMode(false);
},
});
//event handler
const updateList = ({target}) => {
const idx = target.closest('li').dataset.idx;
PatchMutation.mutate(idx);
};
.....
......
Server와 상태 동기화
todo 애플리케이션에서 POST 요청을 보내 새로운 todo를 입력한다고 가정하자. 화면은 언제 업데이트 되고, 서버에는 언제 데이터를 보내서 동기화 해야 하는가? 서버처리를 기다리는 동안 화면의 렌더링은 어떻게 해야 하는가? (ex. loading……)
두개 이상 컴포넌트 영역에서 동일한 endpoint로 부터 데이터를 가져와야 한다면 각각 가져와야 할까? 공통의 상위 컴포넌트에서 데이터를 패칭해야 할까?
Redux 처리 방식
Redux 비동기 데이터 흐름
- middleware 기반으로 중간layer를 추가한다.
- redux-saga, redux-thunk 등의 방법이 있다.
Hooks 처리 방식
useEffect 또는 event handler에서 fetching작업을 해서 data를 가져온 후 rerendering한다.
const UserForm = props => {
const [user, setUser] = useState(props.user)
const form = useRef(null)
const submit = e => {
e.preventDefault()
const data = new FormData(form.current)
fetch('/api', { method: 'POST', body: data })
.then(res => res.json())
.then(json => setUser(json.user))
}
return (
<form ref={form} onSubmit={submit}>
<input type="text" name="user[name]" defaultValue={user.name} />
{user.errors.name && <p>{user.errors.name}</p>}
<input type="email" name="user[email]" defaultValue={user.email} />
{user.errors.email && <p>{user.errors.email}</p>}
<input type="submit" name="Sign Up" />
</form>
)
}
